We use cookies to help us deliver and improve this site. By clicking Confirm or by continuing to use the site, you agree to our use of cookies. For more information see our Cookie Policy.
Useful Information on Circumferential Piston Pumps
What are Circumferential Piston Pumps and why use them?

Circumferential piston pumps (CPP) are self-priming, rotary positive displacement pumps offering a smooth, non-pulsating, low shear flow. The pumps share similar technology with lobe pumps differing only in rotor design. Both are used in food and beverage, dairy, cosmetic and pharmaceutical industries because of their gentle action on shear-sensitive liquids and slurries. Traditionally, rotary lobe pumps have been favoured in Europe and circumferential piston pumps in the US.
How does a circumferential piston pump work?
The ‘pistons’ are not reciprocating, as in a typical piston pump, but are twin rotors independently driven by a motor and gearing system. The rotors are mounted on parallel shafts, turning in opposite directions. The rotors closely follow the curve of the pump casing, travelling in annular-shaped channels machined into the pump body. The wings also run in close clearance with the hub of the neighbouring rotor but there is no direct contact between them. The rotors usually have twin wings although single wing rotors may be preferred for solids transfer.
Suction is generated from an expanding cavity created by the tight clearances and precise interlocking of the rotors opposite the inlet. Pockets of fluid are carried around the outside path of the pump chamber, and expelled at the outlet port. The delivery rate is directly related to pump speed and, for a given feed viscosity, is unaffected by head pressure.
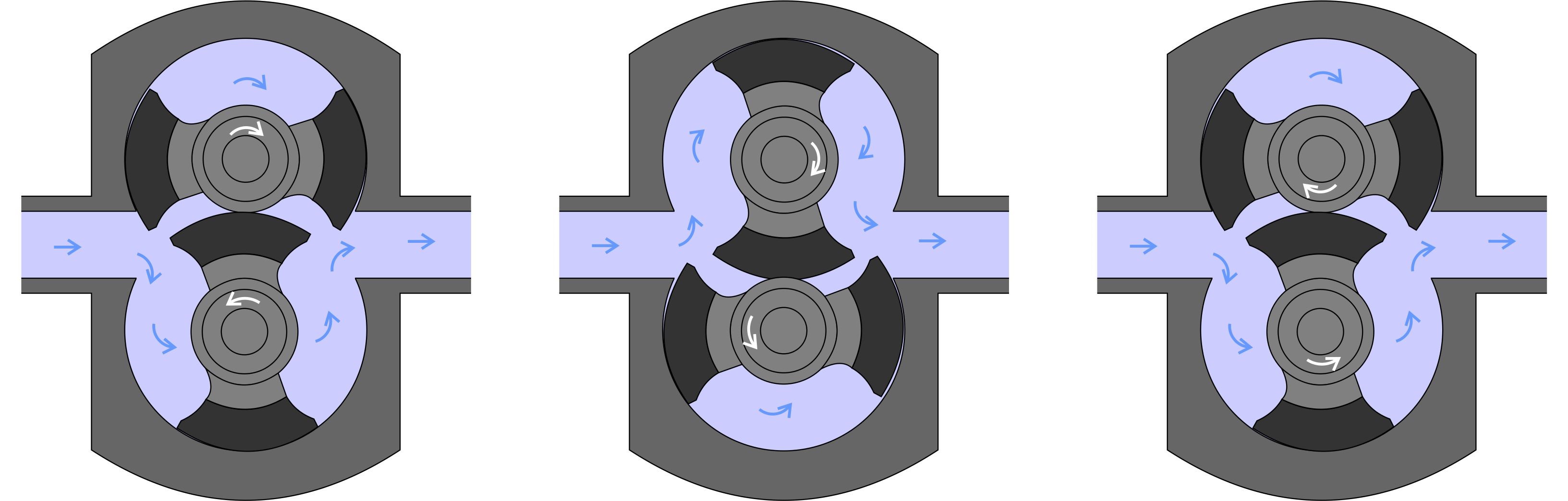
Circumferential piston pump cycle
Construction
Circumferential piston pumps are manufactured to comply with food safety regulations (such as FDA, EHEDG and 3A). Standard features include 316 stainless steel construction, polished surfaces, self-draining, sanitary seals, and easy disassembly for thorough cleaning and sanitation. The rotors are usually manufactured using high quality, non-galling nickel-based alloys because of the tight casing clearances. Available in a range of compositions (often under the trademarks Inconel and Hastelloy), these are resistant to corrosion from a wide range of chemicals including acids and alkalis. Nickel alloys are also strong and can withstand high temperatures and pressures.
Self-priming
The long sealing paths and tight clearances of the circumferential piston rotors produce excellent suction for self-priming.
Slip
In all positive displacement pumps, it is inevitable that a proportion of the pumped fluid leaks back from the discharge side to the suction side. This loss in performance is called ‘slip’. As well as the loss in performance and dosing accuracy, slippage is often a cause of wear, particularly with abrasive fluids. In circumferential piston pumps, slip occurs around the sealing paths between the rotors and case. Slip is a greater problem with low viscosity feeds (‘thin’ fluids) and at higher differential pressures.
Shear Sensitive Liquids
Many different types of fluids (for example: glues, paints, soaps, ketchup) undergo an increase or decrease in viscosity during pumping and, in some cases, this can be damaging, causing separation or setting. Fluids of this type are called shear-sensitive. Generally, shear can be minimized by selecting a circumferential piston pump with large clearances, and by running it very slowly.
Solids
The large cavities between the rotors are advantageous for transporting entrained soft solids. In addition, the rotors are designed with a scooped leading edge which keeps solids away from the rotor/case interface where they might be damaged or cause clogging, jamming or wear.
Cleaning
Circumferential piston pumps normally require COP (clean out of place) and for this reason offer easy disassembly with front panel access. Some models may offer a CIP (clean in place) option.
Summary
Circumferential piston pumps (CPP) are a type of rotary positive displacement pump offering a smooth, non-pulsating, self-priming, low shear flow. They are used for many applications in food, beverage, dairy, cosmetic, and pharmaceutical industries and in applications with high viscosity fluids, or with entrained solids or slurries, or where higher differential pressures and self-priming are important.
 Viking’s Revolution® Series offers circumferential piston rotor configurations.
Viking’s Revolution® Series offers circumferential piston rotor configurations.
Advantages
- Can generate high pressures
- Suitable for viscous fluids, such as oils, syrups and slurries
- Can pass soft solids
- No metal-to-metal contact
- COP/CIP capabilities
- Non-pulsating discharge
- Gentle pumping action
- Self-priming
- Reversible operation
Disadvantages
- Can be more expensive than comparable pump technologies
- Requires regular maintenance
- Reduced lift with thin liquids
- Unsuitable for fluids containing large or abrasive solids
Applications
- Chemical processing
- Paper coatings
- Soaps and surfactants
- Paints and dyes
- Rubber and adhesives
- Pharmaceuticals and cosmetics
- Food applications